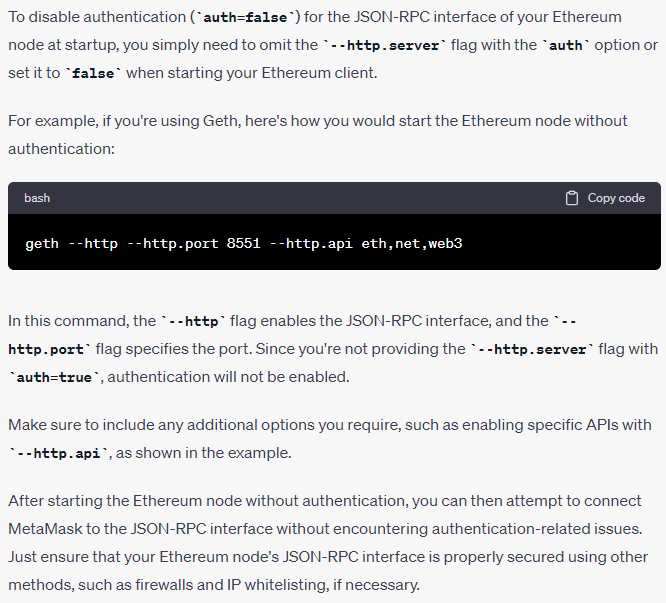
In the context of an Ethereum node’s JSON-RPC interface, setting --http.server to auth=true means that you are enabling authentication for the HTTP-based JSON-RPC server. This means that when you send JSON-RPC requests to the node’s HTTP endpoint, you will need to provide valid credentials for authentication.
Authentication is a security feature that helps protect the JSON-RPC interface from unauthorized access. It ensures that only authorized users or applications are allowed to interact with the Ethereum node’s RPC server.
When you enable authentication with --http.server auth=true, you would typically need to provide an authentication mechanism, such as a username and password or an API token, when making JSON-RPC requests.
For example, if you’re using curl to make a JSON-RPC request with authentication, you might use a command like:
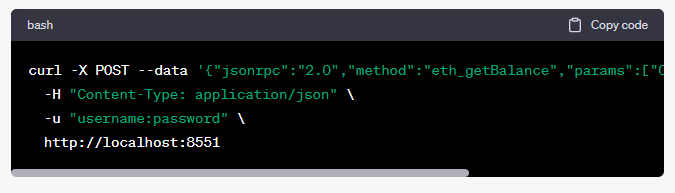
In this example, replace "username" and "password" with the actual credentials you’ve configured for authentication.
By using authentication, you add an additional layer of security to your Ethereum node’s JSON-RPC interface, helping to prevent unauthorized access and potential security breaches. It’s important to configure authentication carefully and store credentials securely.
This auth=true may create problem to connect rpc to MetaMask?
Yes, enabling authentication (auth=true) on your Ethereum node’s JSON-RPC interface can potentially cause connectivity issues with MetaMask. This is because MetaMask might not be set up to provide authentication credentials when connecting to the RPC server.
MetaMask is designed to interact with Ethereum nodes that have open and unrestricted JSON-RPC interfaces. When you enable authentication, MetaMask might not be able to provide the necessary credentials to authenticate itself with the node, resulting in connectivity problems.
If you’re planning to use MetaMask to interact with your Ethereum node, it’s generally recommended to keep the JSON-RPC interface open and not enable authentication. Instead, you can secure the JSON-RPC interface by restricting its access using firewalls, IP whitelisting, and other security measures. This way, you can ensure that only trusted sources can access the interface while still allowing MetaMask to connect seamlessly.
If you’ve already enabled authentication and are experiencing connectivity issues with MetaMask, you might consider disabling authentication or exploring alternative solutions to secure your JSON-RPC interface while maintaining compatibility with MetaMask.